Misoperation and Maintenance Tips of Drilling Rig Kelly Bar
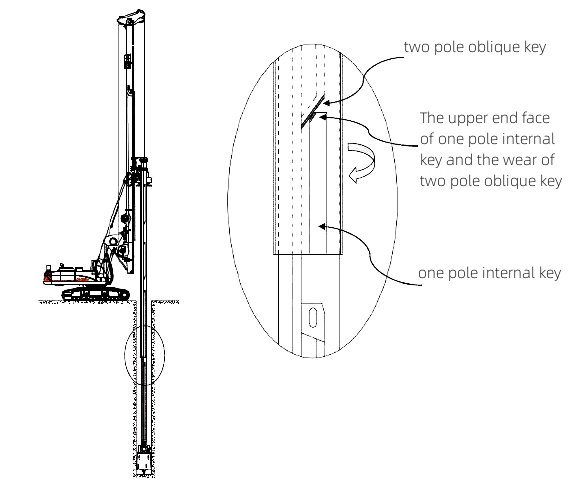
When pressurizing, do not find the pressure point, and use the lock Kelly bar as friction Kelly bar. The contact surface between the internal key of 1 pole and the oblique key of 2 pole is very small. In a short period of time, the upper end face of the internal key of 1 pole and the side face of the oblique key of 2 pole is severely worn, leading to jamming or rolling of the Kelly bar.
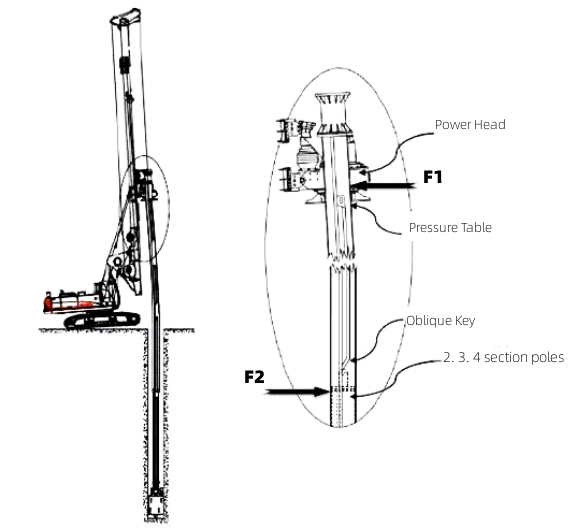
During the operation, the front track of the main machine is lifted, and the mast is backed up. The first section of the mast is subjected to the force F1 from the power head towards the rear. The force required to maintain the verticality of each section of the inner layer is F2. Two forces form a moment to break the first section of the rod. The top group of pressure table and oblique key in the first section of the pole are most likely to be broken.
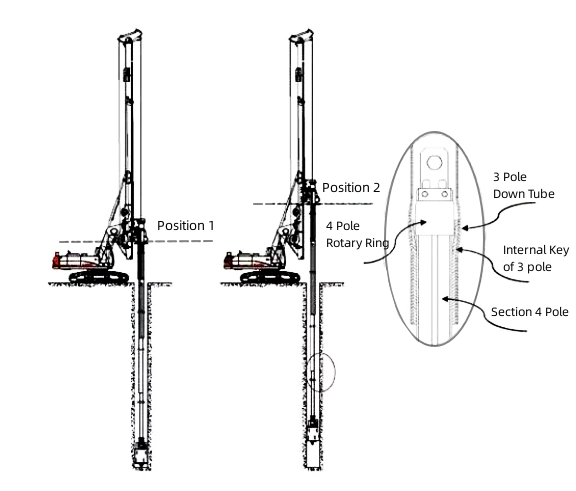
During the process of lowering the Kelly bar, there was no buffering when the adjacent two pipes came into contact. As a result, the internal pole rotating ring collides with the inner key of the outer pole, causing the lower tube of the outer pole to bulge.
Maintenance Measures for Kelly Bar:
1. In ordinary formations, the first inspection cycle:
After the first 50-100 hours of operation of the piling rig, inspect the 4th section of the Kelly bar.
After working for 100-150 hours, inspect the 2nd and 3rd section of Kelly bar.
2. Inspection cycle during normal use:
After every 250 to 300 hours of operation, inspect the 4th section of Kelly bar.
After every 400-500 hours of operation, inspect the second and 3rd sections of Kelly bar.
3. After each shift, clean the sludge on the Kelly bar and thoroughly clean the Kelly bar before starting maintenance work.
Proper maintenance can prevent premature wear of drilling rig Kelly bar, while also helping to repair damaged parts of the Kelly bar and extend its service life.
